Yogyakarta, March 25, 2025 – Theories of Globalization is a mandatory course in the Department of Intercultural Studies that examines the impact of globalization from various perspectives. Globalization is understood as a phenomenon with multiple influences—both positive and negative—on culture, ecology, and the way of life of local communities. Through an interdisciplinary approach, students are encouraged to understand how globalization affects social structures and cultural identities across different parts of the world. By the end of the course, students are expected to have a more balanced perception of globalization and be able to analyze its impact on local cultures. The course is conducted through a combination of lectures, discussions, and presentations, with structured assignments and essay writing as part of the evaluation process.
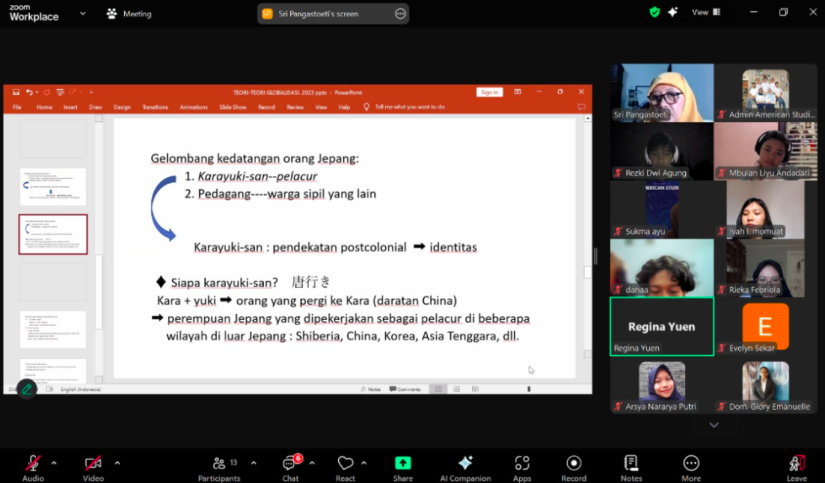
In its sixth session, the course was taught by Dr. Sri Pangastoeti, M. Hum., who explored various academic perspectives on globalization, including studies from Japanese literature. One of the key topics discussed was the karayuki-san phenomenon, the role of geisha, Japan’s isolation policy, and the historical dynamics between Japan and the United States that continue to shape their cultural and political relations today.
One of the often-overlooked impacts of globalization is how the global economic system has influenced migration dynamics and the role of women in history. Labor mobility, whether voluntary or forced, has often been shaped by broader social and economic conditions. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Japan experienced this phenomenon, particularly in the case of women known as karayuki-san.
The karayuki-san phenomenon refers to Japanese women from impoverished areas, particularly Nagasaki, who migrated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries to various countries in Southeast Asia, East Asia, Siberia, and Australia. They worked in various sectors, including entertainment and prostitution. Economic hardship and social pressures forced many young women to be sent abroad as a means of survival. The presence of karayuki-san reflects the complexity of migration in the early stages of globalization, where economic and social factors drove labor mobility across national borders.
The discussion also touched on the differences between geisha and oiran. Geisha are professional artists trained in traditional Japanese arts such as music, dance, and refined conversation. Contrary to common misconceptions outside Japan, geisha are not sex workers but rather cultural performers who preserve Japanese artistic traditions. However, geisha have often been misinterpreted, partly due to inaccurate portrayals in American popular media. Western films and literature have frequently depicted geisha as sex workers or confused them with oiran—high-class courtesans who were not only skilled in the performing arts but also provided sexual services. These stereotypes have been shaped through media framing, which simplifies and distorts the distinctions between different female roles in Japan’s past.
Another significant topic discussed in the lecture was Japan’s isolationist policy, or sakoku, which was enforced during the Edo period under the Tokugawa shogunate (1603–1868). Japan closed itself off from the outside world for more than two centuries, restricting foreign interaction to maintain political and social stability and prevent external influences. This policy only ended when the United States pressured Japan to open its ports for international trade. This event marked a turning point in Japanese history, triggering modernization and integrating the country into the currents of globalization.
Japan’s relationship with the United States continued to evolve but was not always harmonious. In the early 20th century, the United States implemented discriminatory immigration policies against Asians, including the Japanese. One of the most significant was the Immigration Act of 1924, which explicitly banned Japanese immigrants from entering the U.S. This policy was driven by anti-Asian sentiment, concerns over labor competition, and political pressure from white labor groups. Discrimination against Japanese immigrants reflected the global tensions that shaped international relations at the time.
Although Japan-U.S. relations were once marked by conflict—especially during World War II—the dynamic between the two countries continued to develop. After the war, Japan underwent reconstruction with American support, eventually becoming one of the U.S.’s closest allies in the Asia-Pacific region. Beyond economic and political cooperation, cultural exchanges between the two nations have flourished. Traditional Japanese arts have gained widespread recognition in the United States, while American popular culture, such as films and music, has had a significant influence on Japanese society.
This course is taught by a team of lecturers from various academic backgrounds, providing a multidisciplinary approach to understanding globalization. Dr. Sri Pangastoeti offered in-depth insights into how globalization has shaped Japanese culture. The discussions in this lecture emphasized that globalization is not merely about economic and technological exchange but also deeply intertwined with history, identity, and complex cultural dynamics. The interaction between Japan and the United States serves as a concrete example of how globalization shapes international relationships and continuously transforms cultural landscapes.
[Public Relations American Studies, Nariza Ayu Pasha]