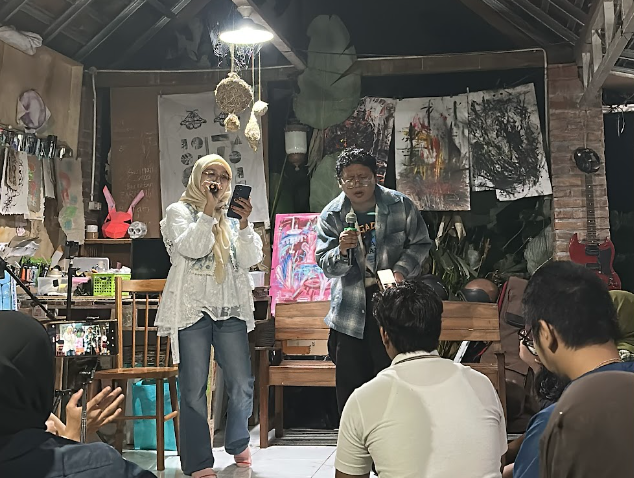
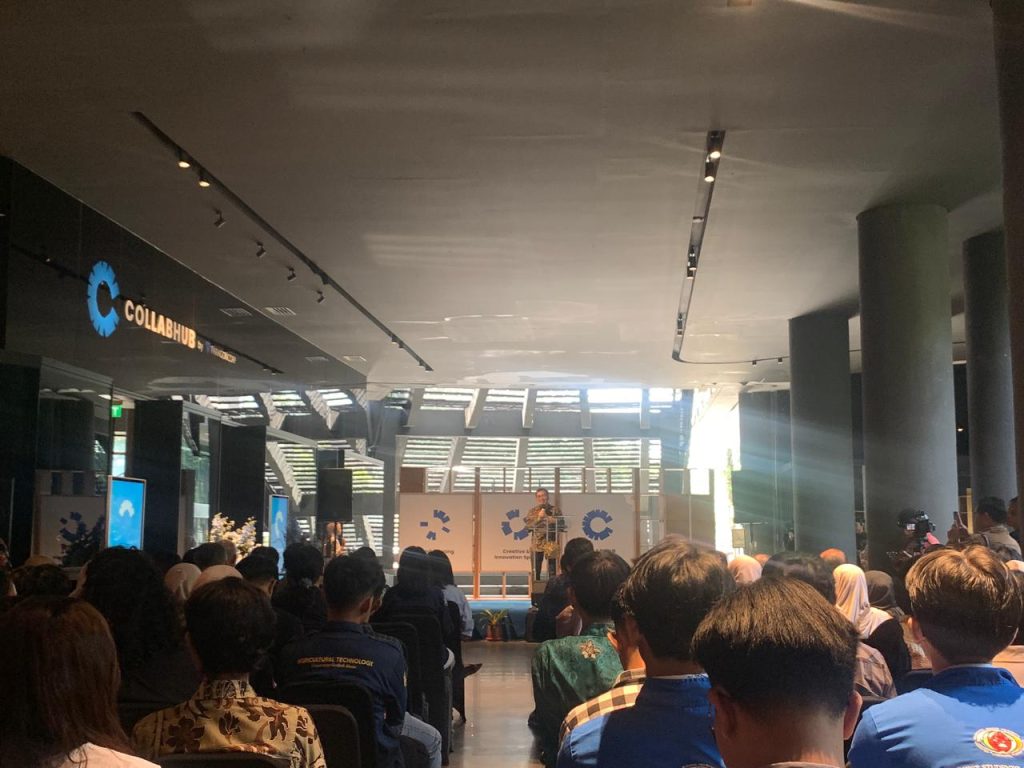
The Master’s Program in Literature at the Faculty of Cultural Sciences, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), held an Inauguration Night for New Students of the Even Semester of the 2025/2026 Academic Year at Pondok As-Salam Kalimasada, Sleman Regency, Yogyakarta, on Saturday–Sunday, 14–15 February 2026. Carrying the theme “Our Literature, One Family,” the event marked the initial momentum in shaping the academic identity of master’s students.
The main session commenced on Saturday at 7:30 p.m. (WIB) and featured the Head of the Master’s Program in Literature, Prof. Dr. Aprinus Salam, M.Hum. In his remarks, he emphasized that at the master’s level, students are expected to demonstrate a higher degree of academic maturity.
“Master’s students are not only required to master course materials. They must also understand the history and philosophy of UGM as the foundation for developing academic attitudes and ethics,” he stated.
Aprinus also highlighted the importance of building a collaborative academic culture. He stressed that an open tradition of discussion, accompanied by mutual support across cohorts, is a prerequisite for fostering a healthy, productive, and sustainable scholarly community.
The event also featured a sharing session with senior students—Khotibul Umam, Marsya Kamila, and Kharisma Qurrota A’yun—who shared their experiences regarding time management, academic dynamics, and strategies for preparing research proposals as initial preparation for graduate studies.
The keynote lecture was delivered by Professor of Philosophy at UGM, Prof. Drs. M. Mukhtasar Syamsuddin, M.Hum., Ph.D., who elaborated on UGM’s Five Pillars as the philosophical foundation of the university. He explained that UGM is grounded in five principal identities: a National University, a University of Struggle, a Pancasila University, a People-Oriented University, and a Center of Culture. These pillars serve as the institutional direction as well as ethical guidelines for the entire academic community.
“UGM is not merely an educational institution, but a space for shaping the nation’s character. Therefore, its core values must be embodied in students’ daily conduct,” he remarked.
During the discussion session, Mukhtasar Syamsuddin also underscored the importance of interdisciplinary openness, particularly for literature students. According to him, the complexity of social and cultural issues demands cross-disciplinary dialogue; therefore, students should not construct rigid boundaries between literature, philosophy, and other fields of study. This perspective is highly relevant to the reflective and humanistic character of literary studies.
The main session concluded at 9:30 p.m. and was followed by performances by the 2025/2026 Even Semester cohort, including poetry readings and musical performances that strengthened solidarity among members. After the evening program, participants rested and continued the agenda the following day.
On the second day, Sunday (15/2), activities began with congregational dawn prayer, followed by a morning walk and group games designed to reinforce togetherness. The event concluded with a session for sharing hopes and a group photo before participants returned to their respective homes.
Through this inauguration night, the Master’s Program in Literature at the Faculty of Cultural Sciences, UGM, reaffirmed its commitment to postgraduate education that is oriented not only toward academic achievement but also toward the cultivation of integrity, interdisciplinary awareness, and moral responsibility in upholding the university’s core values. The event marked the beginning of the intellectual journey of 33 new students in developing critical, reflective literary studies that contribute meaningfully to society.
[Master of Arts in Literature, Rini Febriani Hauri]