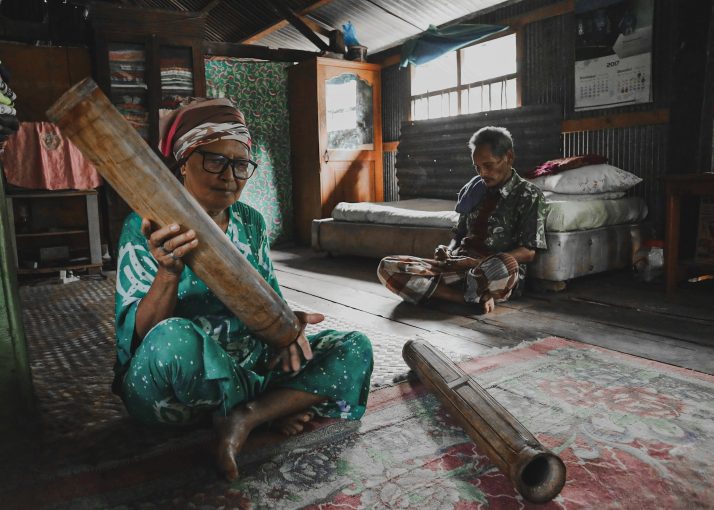
Komodo National Park, as one of Indonesia’s natural treasures, has attracted the attention of tourists from all over the world. However, behind the charm of the islands and the unique fauna that reside within them, there is a deeper story about the Ata Modo tribe, which has been impacted by the rapid development of the tourism industry in the region. The Ata Modo tribe itself is a community that has inhabited the island of Komodo for a long time, even before the establishment of Komodo Island as the Komodo National Park. With the designation of Komodo National Park and the influx of tourism activities, the Ata Modo tribe experienced changes in their socio-cultural activities. One of them is the shift in the livelihood of the Ata Modo tribe.
The socio-cultural dynamics that occur in the Ata Modo tribe have been seen and investigated in the latest research by a research team that is part of the Student Creativity Program in Social Humanities Research (PKM-RSH) in 2023. This research team is called AtaModo UGM, consisting of Arif Putra Pratama (Faculty of Law 2020), Avicenna Elang (Faculty of Law 2021), An Nuur Khairune Nisa (Faculty of Cultural Sciences 2021), and Noor Risa Isnanto (Faculty of Cultural Sciences 2021). The research team was accompanied by an accompanying lecturer, namely Dr. Dian Agung Wicaksono, S.H., LL.M. The research was conducted in approximately one week using participant observation methods, in-depth interviews, and searching for secondary sources from various literature and legislation.
The research entitled “Coercive Transformation of Indigenous Peoples: Marginalization of the Komodo Tribe Amid the Hegemony of Komodo National Park Tourism Development” seeks to find out about three things related to the social, cultural, and economic conditions of the Ata Modo tribal community. The research team succeeded in getting direct answers from the Ata Modo tribal community regarding three problem formulations. First, the Ata Modo tribe has cultural potential that can still be maintained and developed according to the needs of the Ata Modo tribe community and related parties who are interested in collaborating. By discovering the cultural potential that still exists in the Ata Modo tribe, the research team realized that this was to Koentjaraningrat’s theory regarding the seven elements of culture consisting of language, knowledge system, social organization, technology, livelihood system, belief system, and art. Second, it was discovered that until now there has been no legal determination of Komodo Village as a Customary Law Community or designation of a Traditional Village, this could result in a conflict of interest and the overriding of the traditional rights of the Ata Modo tribal community. Third, the arrival of the Komodo National Park and the tourism industry has made the Ata Modo tribal community experience a coercive transformation in social, cultural, and economic aspects.
Therefore, through this research, the PKM-RSH team hopes that these findings will provide valuable understanding and considerations for all parties involved in developing Komodo National Park tourism. In this context, special focus is given to the Ata Modo Tribe which is the center of attention, so that they can be actively involved in efforts to protect their cultural heritage and local wealth. This approach is also in line with the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) number 11 regarding sustainable city and community development, in which the Ata Modo Tribe, as a community that has long lived on Komodo Island, also plays an important role.
Writer: Member of the UGM PKM-RSH AtaModo Team